Control and Coordination
control and coordination mechanisms in both humans and plants. It begins with a detailed overview of the human nervous system, highlighting its central and peripheral components, and delves into the anatomy and functions of the human brain, including the cerebrum, cerebellum, medulla oblongata, and hypothalamus. The article also covers how plants coordinate their responses to stimuli through hormones such as auxins, gibberellins, cytokinins, ethylene, and abscisic acid. It further discusses the roles of various animal hormones like insulin, adrenaline, thyroxine, growth hormone, testosterone, and estrogen in maintaining bodily functions and homeostasis. In addition, the article includes a set of 15 questions and answers to reinforce the key concepts covered, making it an excellent resource for students and anyone interested in understanding the complex processes of control and coordination in living organisms.
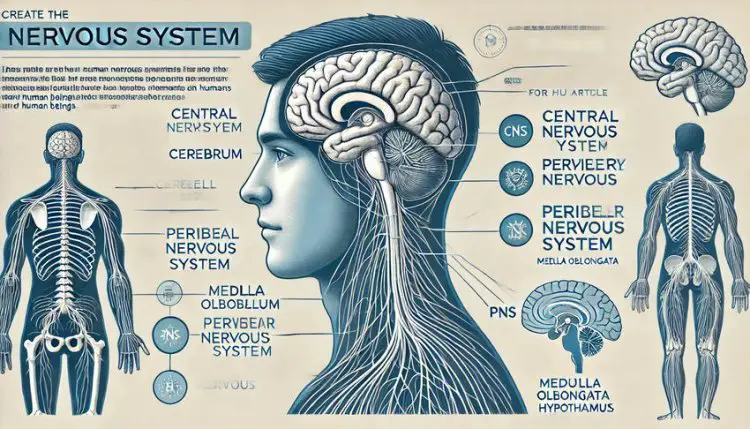
The Nervous System of Human Beings
The nervous system in human beings is a complex network of nerves and cells that carry messages to and from the brain and spinal cord to various parts of the body. The main components are:
- Central Nervous System (CNS): Consists of the brain and spinal cord.
- Peripheral Nervous System (PNS): Consists of all the nerves that branch out from the brain and spinal cord.
Anatomy of the Human Brain
The human brain is divided into several parts, each with specific functions:
- Cerebrum: The largest part of the brain responsible for voluntary actions, intelligence, memory, and sensory processing.
- Cerebellum: Controls balance, coordination, and fine muscle control.
- Medulla Oblongata: Regulates vital functions like heartbeat, breathing, and blood pressure.
- Hypothalamus: Maintains homeostasis by regulating body temperature, hunger, and thirst.
Coordination in Plants
Plants coordinate their responses to stimuli using hormones. The main plant hormones are:
- Auxins: Promote cell elongation and are involved in phototropism and gravitropism.
- Gibberellins: Stimulate stem elongation, seed germination, and flowering.
- Cytokinins: Promote cell division and delay aging of leaves.
- Ethylene: A gas that promotes fruit ripening and leaf abscission.
- Abscisic Acid (ABA): Inhibits growth and promotes seed dormancy.
Hormones in Animals
Hormones in animals are chemical messengers secreted by endocrine glands. Key hormones include:
- Insulin: Regulates blood glucose levels.
- Adrenaline: Prepares the body for 'fight or flight' responses.
- Thyroxine: Regulates metabolism.
- Growth Hormone: Stimulates growth and cell reproduction.
- Testosterone: Regulates male secondary sexual characteristics.
- Estrogen: Regulates female secondary sexual characteristics.
Top 15 Questions and Answers
-
What are the two main parts of the central nervous system?
The brain and the spinal cord.
-
What is the function of the cerebrum?
The cerebrum is responsible for voluntary actions, intelligence, memory, and sensory processing.
-
How do auxins affect plant growth?
Auxins promote cell elongation and are involved in phototropism and gravitropism.
-
What is the role of insulin in the body?
Insulin regulates blood glucose levels.
-
What does the medulla oblongata regulate?
The medulla oblongata regulates vital functions like heartbeat, breathing, and blood pressure.
-
Which hormone is responsible for fruit ripening in plants?
Ethylene is responsible for fruit ripening.
-
What hormone is secreted by the adrenal glands in response to stress?
Adrenaline is secreted in response to stress.
-
How does the hypothalamus maintain homeostasis?
The hypothalamus regulates body temperature, hunger, and thirst to maintain homeostasis.
-
What is the function of thyroxine?
Thyroxine regulates metabolism.
-
What role does gibberellin play in plants?
Gibberellins stimulate stem elongation, seed germination, and flowering.
-
What is the effect of abscisic acid (ABA) in plants?
ABA inhibits growth and promotes seed dormancy.
-
Which hormone promotes cell division in plants?
Cytokinins promote cell division in plants.
-
What is the function of the cerebellum?
The cerebellum controls balance, coordination, and fine muscle control.
-
Which hormone regulates male secondary sexual characteristics?
Testosterone regulates male secondary sexual characteristics.
-
What does growth hormone stimulate?
Growth hormone stimulates growth and cell reproduction.
What's Your Reaction?





















